wsrp
SQL Injection
SQL Injection (SQLi) is a critical web security vulnerability that occurs when an attacker can manipulate a web application’s database queries by injecting malicious SQL code into input fields. This happens when applications directly concatenate user input into SQL queries without proper sanitization or parameterization. In this project, we demonstrate a vulnerable login endpoint that allows SQL injection attacks.
Testing the Vulnerability
To test the SQL injection vulnerability:
- Navigate to the SQL injection vulnerable login endpoint (
/api/sqli_vuln/auth/login) - Try these example payloads in the username field:
' OR '1'='1 admin' -- ' UNION SELECT * FROM users -- - Any password can be used as the injection is in the username field
- The application will execute the manipulated SQL query, potentially exposing sensitive data
Here is a request that takes advantage of an endpoint in the server that is vulnerable to SQL injection:
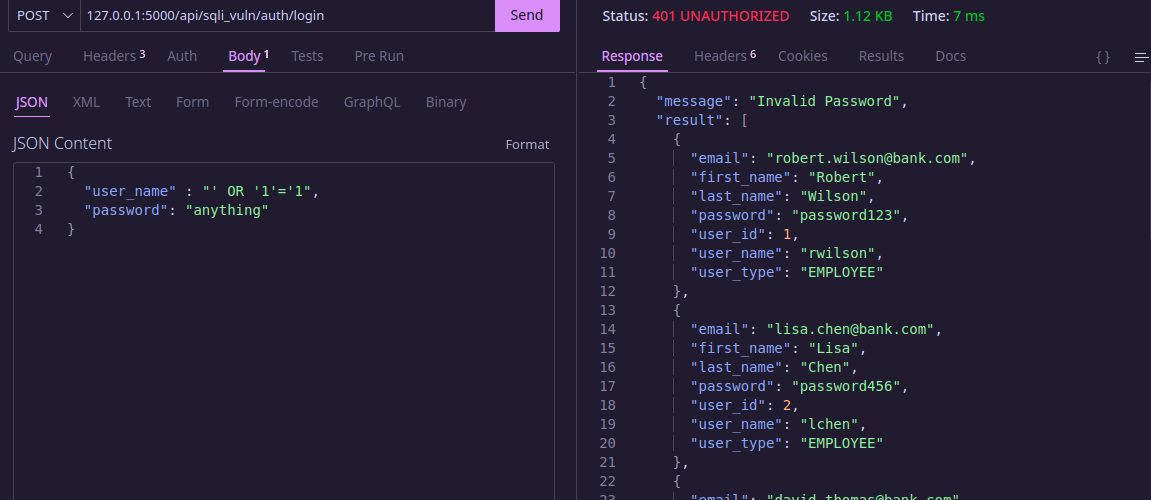
This example is convoluted and obviously staged, but it shows how an attacker may be able to insert characters into a request to manipulate the SQL query that the server is running. In this case, the attacker is able to insert a ‘ character into the request, which causes the SQL query to be malformed. The attacker can then use this to manipulate the query to return all of the users in the database, which is a huge security risk.
Why This Is Dangerous
SQL injection vulnerabilities are among the most severe security risks because:
- Attackers can bypass authentication entirely
- Entire databases can be exposed, downloaded, or destroyed
- Attackers can execute administrative operations on the database
- Confidential data can be stolen, including:
- User credentials
- Personal information
- Financial data
- Business secrets
The impacts can include:
- Data breaches exposing user information
- Financial fraud through unauthorized access
- System compromise through elevated privileges
- Regulatory compliance violations
- Complete system takeover in some cases
- Permanent data loss if records are deleted
To prevent SQL injection:
- Always use parameterized queries
- Implement proper input validation
- Use an ORM (Object-Relational Mapping) system
- Apply the principle of least privilege for database users
- Regular security audits and testing
The secure version of any database operation should never directly concatenate user input into SQL queries.